
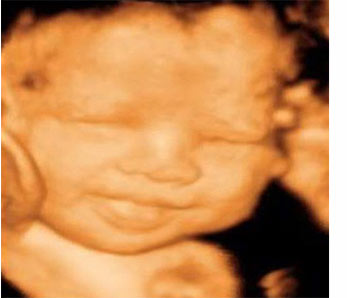
4D ultrasound also helps with prenatal diagnosis of congenital abnormalities, although genetic diseases can only be detected by studying the karyotype (the chromosomal pattern of an individual). With the 4D ultrasound, it is possible to visualise the baby’s face much earlier than this, making an early pregnancy scan more useful. In addition to obtaining and displaying images in the same way as 3D, 4D ultrasound captures images in real time.ĭuring a pregnancy, you will generally have a 12 week ultrasound, although generally, they should be done between weeks 20 and 22. It is possible to evaluate cranial sutures, look bone fractures and detect subtle anomalies of the vertebrae. Other advantages of 3D and 4D ultrasound over 2D are that it is possible to study musculoskeletal malformations more closely, undertake an evaluation of facial dimorphism and also study abnormalities in hands and feet. Even so, these ultrasounds involve additional training and also require an important technological investment. This makes it possible for patients to recognise the images that appear on the monitor, which was not the case with 2D ultrasounds, when only the specialist was able to interpret the images.

What are the differences between 2D, 3D and 4D ultrasound?ģD and 4D ultrasounds allow imaging and three-dimensional analysis. The ultrasound machine is the source of the sound waves and also collects them to produce them as visual images on a screen. When sound hits a surface that can reflect it, the sound (or echo) is bounced back to the source. What is ultrasound used for? An ultrasound scan is a diagnostic technique which has many purposes though it is typically used by a gynaecologist to monitor the foetus in the mother's womb during pregnancy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
